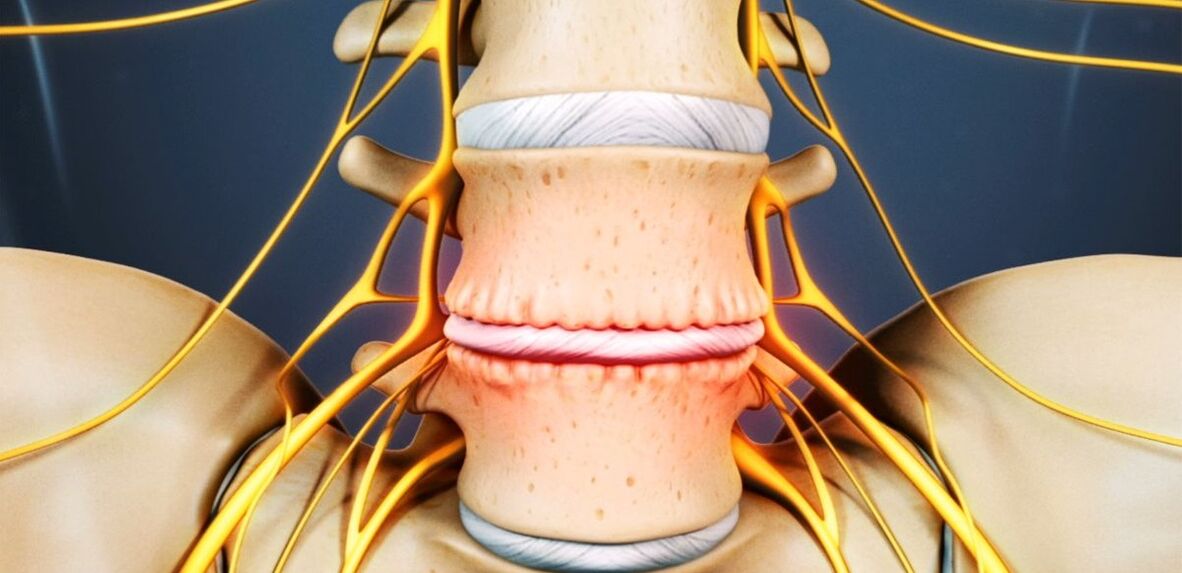
Osteochondrosis is a chronic degenerative-dystrophic disease that develops under the influence of many different factors. Initially, pathological changes occur in the pulposus nucleus (inner contents of the vertebral disc) and then spread to the fibrous ring (outer shell of the disc) and other elements of the spinal motion segment (SDS). This can be the result of the body's natural aging process, or it can occur against the background of injuries, increased loads on the spine and other causes. In any case, osteochondrosis is only the first stage of destruction of the intervertebral disc, and if left untreated, often develops protrusions and hernias that require surgical removal.
The intervertebral disc is the formation of cartilage that separates the vertebral bodies and acts as a shock absorber.
Lumbar osteochondrosis: what is it
48-52% of people suffer from osteochondrosis. And lumbar osteochondrosis is the most common. The disease can affect any, some or even all of the intervertebral discs of the lumbosacral spine. L5-S1, L4-L5, and to a lesser extent L3-L4 disks often suffer. The upper lumbar discs (L3-L2 and L2-L1) are less affected.
The prevalence of lumbar osteochondrosis is associated with the greatest load falling on the lumbar region during any physical activity, especially lifting and carrying weights, walking, running, and sitting. The lumbar vertebrae consist of 5 vertebrae that are much larger than the thoracic and cervical vertebrae. Accordingly, the intervertebral discs that separate them become larger. Normally, there is a slight anterior curvature (physiological lordosis) in the lumbar region. It is the last mobile part of the spine and is adjacent to the stable sacrum, so it is most often referred to as lumbosacral osteochondrosis.
If in the past osteochondrosis was considered an age-related disease, today its first manifestations can be observed at the age of 15-19 years. More than 1. 1% of people over the age of thirty suffer from severe symptoms of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs. Clinical manifestations of the disease are already present in 82. 5% of the elderly (over 59 years). At the same time, the frequency of pathology continues to increase, which is mainly due to the increase in the average age of the country's population, but also to lifestyle changes that are not for the better.
Reasons for development
Today, there is still no consensus on the etiology of degenerative diseases of the spine. Nevertheless, the basic theory of their development is attractive. According to him, osteochondrosis is the result of previous damage to the intervertebral disc and bone structures of the spine, inflammatory and other processes. The theory is that degenerative changes are genetically predetermined and in fact inevitable. And their clinical manifestations are associated with the influence of various endogenous and exogenous factors, especially in young and middle-aged people.
Thus, the development of lumbar osteochondrosis is facilitated by:
- heavy physical labor, especially in connection with lifting heavy loads;
- sedentary, sedentary lifestyle;
- bruises, including any back injury;
- overweight;
- metabolic disorders;
- posture disorders, spinal deformities;
- flat feet and other foot pathologies;
- pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancies.

Pathogenesis
Regardless of the cause, degeneration of the intervertebral disc occurs when the intensity of the catabolic processes of matrix proteins (breakdown and oxidation of molecules) begins to exceed the rate of their formation. One of the key points in this process is the malnutrition of the intervertebral discs.
As with most cartilage in adults, because they do not have a direct blood supply, they are deprived of blood vessels, so the supply of nutrients to them and the removal of metabolic products occur by diffusion by successive compression and relaxation of the disc. movement. The main structure that supplies power to the disk are the end plates on its upper and lower surfaces.
The end plates are two-layered, consisting of cartilage and bone tissue cells. Accordingly, on the cartilaginous side they are attached to the disc, and the bone to the vertebral bodies. They are distinguished by a fairly good permeability, which ensures the metabolism between the cells, the intercellular substance of the disc and the blood vessels passing through the vertebral bodies. Over the years, especially under the negative influence of external and internal factors, the structure of the end plates changes and their blood supply decreases, which leads to a decrease in the intensity of metabolism in the intervertebral disc. As a result, its ability to produce a new matrix is reduced, which leads to a gradual decrease in density with age.
At the molecular level, this is accompanied by:
- reduction of diffusion rate of nutrients and metabolic products;
- decrease in cell viability;
- accumulation of cell decay products and modified matrix molecules;
- decrease in the production of proteoglycans (high-molecular compounds responsible for the formation of new cartilage cells and the main sources of synthesis of chondroitin sulfates);
- collagen skeletal damage.
Possible results
As a result of ongoing changes, the intervertebral disc becomes dehydrated and loses its ability to adequately distribute the load on the pulposus nucleus. Therefore, the pressure inside the disc is uneven, and therefore the fibrous ring is overloaded and compressed in several places. As this happens with every human movement, the ring is constantly subjected to mechanical pressure. This leads to negative changes in him.
Also, a decrease in disc height and elasticity often leads to compensatory changes in adjacent vertebral bodies. Bone growths called osteophytes form on their surface. They tend to increase in size over time and even merge with each other, excluding the possibility of movement in the affected PDS.
Because nutrition causes damage to the collagen skeleton, the normal structure of the fibers that form the fibrous ring is disrupted under the influence of pressure at certain points in the pulp nucleus. In the absence of intervention, this eventually causes them to crack and break. Gradually, more and more fibers of the fibrous ring are torn where pressure is applied, causing it to come out. This is facilitated by increasing loads, especially on the spine. And the lumbar region suffers the most because it carries the main load during movement and any physical activity.
The protrusion of the intervertebral disc without the final rupture of the fibrous ring and the size of the base is larger than the protruding part is called the protrusion. An intervertebral hernia is diagnosed with a complete rupture in one place or another.
With the destruction of part of the fibers of the fibrous ring, the pressure on the disk gradually decreases, which leads to a decrease in tension and the fibers themselves. This leads to a violation of its fixation and, consequently, to the pathological mobility of the affected spinal segment.
The motor segment of the spine (SMS) is a structural and functional unit of the spinal column formed by the intervertebral disc, adjacent vertebral bodies, their facet joints, ligaments, and muscles attached to these bone structures.
Normal functioning of the spine is possible only with the proper functioning of the PDS.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
The disease can be asymptomatic for a long time, and then begins to manifest itself as a slight discomfort in the lower back, gradually intensifying. However, in some cases, lumbar osteochondrosis begins acutely, immediately provoking severe pain syndrome. In most cases, the symptoms of the pathology first appear after 35 years.
Back pain is the main symptom of the disease. It can be different in character and can be both painful and dull, sharp, constant or episodic. However, mainly for pathology, especially in the early stages of development, changes in periods of exacerbation and remission are characteristic, and both hypothermia and lifting of a heavy object or unsuccessful, sudden movement can lead to another deterioration of well-being.
The pain is often accompanied by a feeling of numbness and tension in the back muscles. They are aggravated by physical exertion, sudden movements, lifting heavy loads, bending, and even coughing and sneezing.
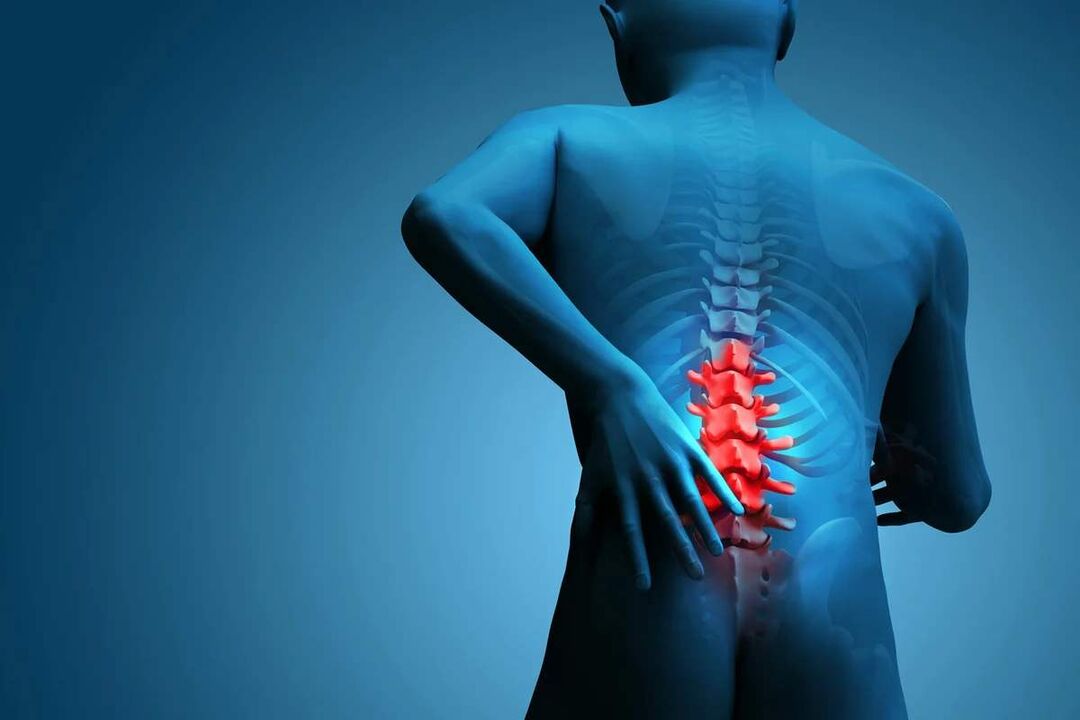
If the nerve root extending from the spinal cord due to the instability of the spinal cord is compressed by one or another anatomical structure, it will lead to the development of relevant neurological disorders. Their main manifestations are:
- fever, severe pain in the sacrum, hips, lower extremities or perineum;
- sensitivity disorders of varying severity;
- movement restrictions, lameness;
- weakness in the muscles innervated by the compressed nerve.
In the lumbar vertebrae, the spinal cord ends at the level of 1-2 vertebrae and passes into a part called the cauda equina, which is formed as a result of the accumulation of spinal roots. Moreover, each of them is responsible not only for the innervation of the muscles, but also for the special organs of the small pelvis, so long-term compression can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the relevant organ. This can lead to impotence, infertility, gynecological diseases, hemorrhoids and other disorders.
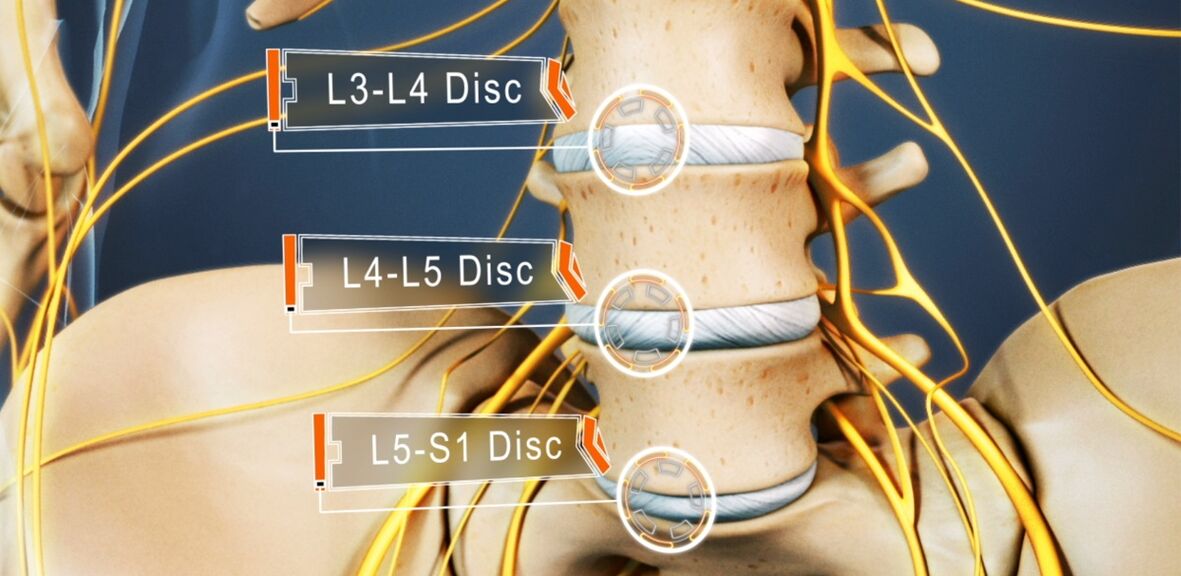
The clinical picture of lumbar osteochondrosis, especially a long course and the occurrence of compression of the spinal roots, depends mainly on the level of the lesion, ie which disc is exposed to degenerative-dystrophic changes.
- Defeat of the L3-L4 disc - pain is transmitted to the anterior-inner parts of the thigh, lower leg and inner ankle. This is accompanied by a decrease in the sensitivity of the anterior surface of the thigh, a decrease in the severity or loss of knee flexion, as well as a decrease in the strength of the quadriceps muscle.
- L4-L5 disc failure - pain is transmitted from the upper thigh to the outer parts of the thigh and lower leg. In rare cases, this is accompanied by the spread of pain in the back of the feet, including 1-3 toes. There is a decrease in sensitivity and muscle weakness in these areas. Sometimes malnutrition and incomplete elongation of the thumb develop.
- L5-S1 disc injury - the pain starts in the middle zone of the thigh and descends to the heel along the back or posterior surface of the thigh and lower leg and can cover the outer edge of the foot like 4-5 toes. Decreased sensitivity is observed in these areas of the lower extremities, and the gastrocnemius and gluteus maximus are often reduced in size, which is accompanied by their weakness. If the spinal cord passing through this PDS level is affected, a decrease or loss of Achilles and plantar reflexes may be observed.
L1-L2 and L2-L3 discs are rarely affected.
The pain that accompanies the disease limits a person and significantly reduces the quality of life. Because they last a long time and are repeated regularly, if they do not always exist, it can not but affect the psycho-emotional state. As a result, more than half of patients suffer from chronic emotional stress, depressive disorders, etc.
Diagnostics
If you have symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis, you should contact a neurologist or vertebrologist. First of all, the doctor considers the nature of the complaints, the characteristics of the pain, the conditions of their occurrence and reduction, the characteristics of the person's working life, and so on.
The second stage of the diagnosis, which is part of the first consultation with a doctor, is a physical examination. During it, the doctor determines the condition of the skin, posture, the depth of the physiological curves of the spine, the presence of curvature, etc. evaluates. The condition of the muscles surrounding the spinal column, called the paravertebral, is definitely assessed because they are often painful and extremely tense, a reflex reaction of the body to inflammation and discogenic pain.
Based on the information obtained during the examination and questioning of the patient, the neurologist may suspect the presence of lumbar osteochondrosis. However, the severity of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral disc and the involvement of bone structures, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are required to exclude possible accompanying pathologies, as well as to confirm the diagnosis and accurately determine the extent of damage.

Laboratory diagnostics
Different types of tests are not decisive in the diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis. They are more focused on assessing the degree of the inflammatory process and the detection of accompanying disorders.
Thus, they can be assigned:
- UAC;
- OAM;
- blood test for blood sugar levels;
- blood chemistry.
Instrumental diagnostics
All patients with suspected lumbar osteochondrosis have the following:
- lumbar radiography in two projections - to determine the structure of bone structures, anomalies, formed osteophytes, changes in facet joints, etc.
- CT - allows to detect changes in bone structure at an earlier stage of development than X-rays, as well as to identify indirect signs of osteochondrosis;
- MRI is the best way to diagnose pathological changes in cartilage formations and other soft tissue structures, which allows to detect the smallest changes in the intervertebral discs, ligaments, blood vessels and spinal cord and accurately assess their severity and potential risks.
In addition, it may be recommended:
- densitometry - a method for determining bone density, which allows you to diagnose osteoporosis, especially in the elderly;
- myelography - allows you to assess the condition of the CSF pathways of the spinal cord and the degree of damage to the protruding disc, which is especially important in the presence of an already formed intervertebral hernia of the spine.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
When osteochondrosis is diagnosed, conservative therapy is usually prescribed to all patients initially in the absence of overt and progressive neurological deficits. But his character is seriously chosen individually.
Because the disease is chronic and the regenerative capacity of the intervertebral discs is extremely limited, especially with overt degenerative-dystrophic changes, the main goals of therapy are to stop their further development and eliminate the symptoms that bother the patient. Therefore, treatment is always complex and includes:
- drug treatment;
- hand therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy.
In the acute period, patients are advised to limit physical activity or even adhere to bed rest for 1-2 days. This will help relax the muscles and reduce the pressure inside the disc. If you need to sit, walk or exercise for a long time, you should wear a stabilizing waist corset.

After the end of the acute period and during remission of the disease, on the contrary, it is important to move as much as possible, but with caution and excluding increased stress in the lumbar region. Patients must acquire the skills of proper sitting, lifting objects from the ground, carrying heavy loads, as all this affects the course of the pathology. After bending the knees, it is important to avoid bending and sudden movements, to lift something from the floor or low surfaces, not to bend down. You should only sit with your back straight in a chair that supports your back well. In addition, it is important to take regular breaks for short workouts during sedentary work. It is important to avoid falling, jumping, running fast and hypothermia.
With osteochondrosis, it is important to maintain an optimal body weight, and for obesity, a diet and exercise appropriate to the patient's condition is indicated, because excess weight creates an increased load on the lumbar region and leads to faster progression of pathological changes. disks.
On average, conservative therapy is usually prescribed for 1-3 months, although it may take longer. However, even after completing the basic course prescribed by your doctor, you should continue to take a number of medications, exercise therapy, and follow lifestyle recommendations.
Medical therapy
The main components of drug therapy are drugs selected individually from the group of NSAIDs. In choosing them, the doctor takes into account not only the severity of the pain syndrome and the course of the inflammatory process, but also the nature of the accompanying diseases, especially the digestive system, as long-term use of NSAIDs can adversely affect their condition. causes exacerbation of various pathologies of the mucous membranes and digestive system.
NSAIDs should be used for acute lower back pain and immediately after their onset. Preferably within 1-2 days. Depending on the severity of the patient's condition, they can be administered intramuscularly, rectally suppositories, topical agents and orally. Admission period should not exceed 2 weeks. In the future, an individually selected drug is required, but often tries to avoid its use.
Recently, drugs have been preferred as an active ingredient containing selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2.
Also, patients are prescribed drugs of the following groups:
- muscle relaxants - help to relax extremely tense muscles and thus reduce back pain;
- chondroprotectors - improve the course of metabolic processes in the intervertebral disc (especially effective in the early stages of development of lumbar osteochondrosis);
- B vitamins - help improve nerve conduction;
- Antidepressants and anxiolytics - used for long-term osteochondrosis, which causes depression, chronic fatigue and other psychological disorders.
Therapeutic blockades are performed with very severe pain, especially of neurological origin. They involve the use of anesthetics in combination with corticosteroids at points near the constricted nerve that cause rapid pain relief. However, the procedure can only be performed by specially trained medical staff in a medical facility, as this is associated with a risk of complications.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy not only improves the quality of blood circulation in the affected area, but also significantly reduces the severity and duration of pain in osteochondrosis. This effectively relieves muscle tension and allows you to remove functional blocks that significantly increase mobility in the affected SMS.
Also, well-performed manual therapy can not only increase the distance between the vertebrae, return them to their anatomically correct position, but also release the compressed nerve roots. As a result, the pain is quickly eliminated and neurological disorders are eliminated. It also reduces the likelihood of complications and disorders of the internal organs.
Additional positive features of manual therapy are improving mood, strengthening immunity, activating the body's natural recovery mechanisms and increasing efficiency. Significant improvement in well-being is usually observed after the first session, and the effect becomes more pronounced in the future. As a rule, the course consists of 8-15 sessions, and it is important to complete it, even with the full normalization of well-being.
Physiotherapy
Courses of physiotherapeutic procedures are shown after the reduction of acute inflammation, which not only helps to reduce pain, but also improves the course of microcirculation, nutrition and reparative processes in the field of degenerative-dystrophic changes. Often prescribed to patients:
- electrophoresis with the use of drugs;
- electrical neuromyostimulation;
- ultrasound therapy;
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy;
- UHF.
Which specific methods of physiotherapy will work best, the frequency of their implementation, the duration of the course and the possibility of combining them with other types of exposure are determined individually for each patient.

In lumbar osteochondrosis, traction therapy gives very good results. Thanks to it, it is possible to increase the distance between the vertebral bodies, which immediately reduces the load on the affected discs. After the session, the patient should wear an orthopedic corset to reinforce the results.
exercise therapy
Once the acute pain has resolved, the treatment program must be completed with exercise therapy. Its main functions are to stretch the spine and relax the spasmodic muscles of the lower back. Therapeutic exercises also help to strengthen the muscle corset, create reliable support for the spine and improve posture. In the process, blood circulation inevitably becomes active and metabolic processes improve, which has a beneficial effect on the nutrition of the discs.
An individual set of exercises is selected for each patient according to the degree of degenerative-dystrophic changes, the patient's level of physical development, the nature of the accompanying disorders, age and other factors. It is recommended that you first study under the guidance of an experienced exercise therapy instructor.
It is recommended that all patients with degenerative changes in the spine visit the pool 2-3 times a week, because swimming lessons minimize the load on the spine, but allow you to effectively strengthen the back muscles.
Thus, osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is one of the most common diseases. At the same time, it can lead to long-term disability and even disability due to the development of complications. Therefore, it is important not to ignore the first signs of the disease, when it is easiest to fight. You should contact a neurologist as soon as possible with the appearance of pain and further numbness, limited mobility, back pain, get the necessary examination and start treatment. In this situation, it will be possible to stop the pathological process and return to normal, full exercise without pain and significant restrictions.